Automating Application Deployment with Portainer CE

Automating Application Deployment with Portainer CE
In today’s fast-moving development environment, automation has become a crucial part of application deployment and lifecycle management. Portainer CE (Community Edition) offers a powerful, user-friendly interface to simplify containerized application deployment on Docker, Kubernetes, and other orchestrators. By combining Portainer with automation workflows, teams can reduce manual overhead, minimize errors, and achieve faster release cycles.
Why Portainer CE for Automation?
Portainer CE provides a centralized control plane for managing containers, images, volumes, networks, and stacks. Its key advantage lies in making container technologies more accessible, especially for teams that prefer a GUI-driven approach. With automation integrated, it bridges the gap between ease of use and operational efficiency.
Key benefits include:
- Declarative Deployment: Define and deploy application stacks via templates or configuration files.
- CI/CD Integration: Automate deployments by linking Portainer with external CI/CD pipelines.
- API-Driven Workflows: Leverage Portainer’s API to trigger deployments, monitor containers, and manage resources programmatically.
- Reduced Complexity: Standardize deployments across environments without deep Docker or Kubernetes expertise.
Automating Deployment with Stacks
Portainer CE allows deployment automation using stack files (docker-compose.yml or Kubernetes manifests). Instead of manually setting up containers, you can store these files in Git repositories and connect Portainer directly. This enables:
- Version Control for deployment configurations.
- Rollback Mechanisms by switching to previous versions.
- Consistency across development, staging, and production environments.
Integrating Portainer CE into CI/CD Pipelines
Automation goes a step further when Portainer is integrated with CI/CD tools such as GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins. A typical pipeline might:
- Build and push Docker images to a registry.
- Update the stack configuration in a Git repository.
- Trigger Portainer’s API to redeploy the stack.
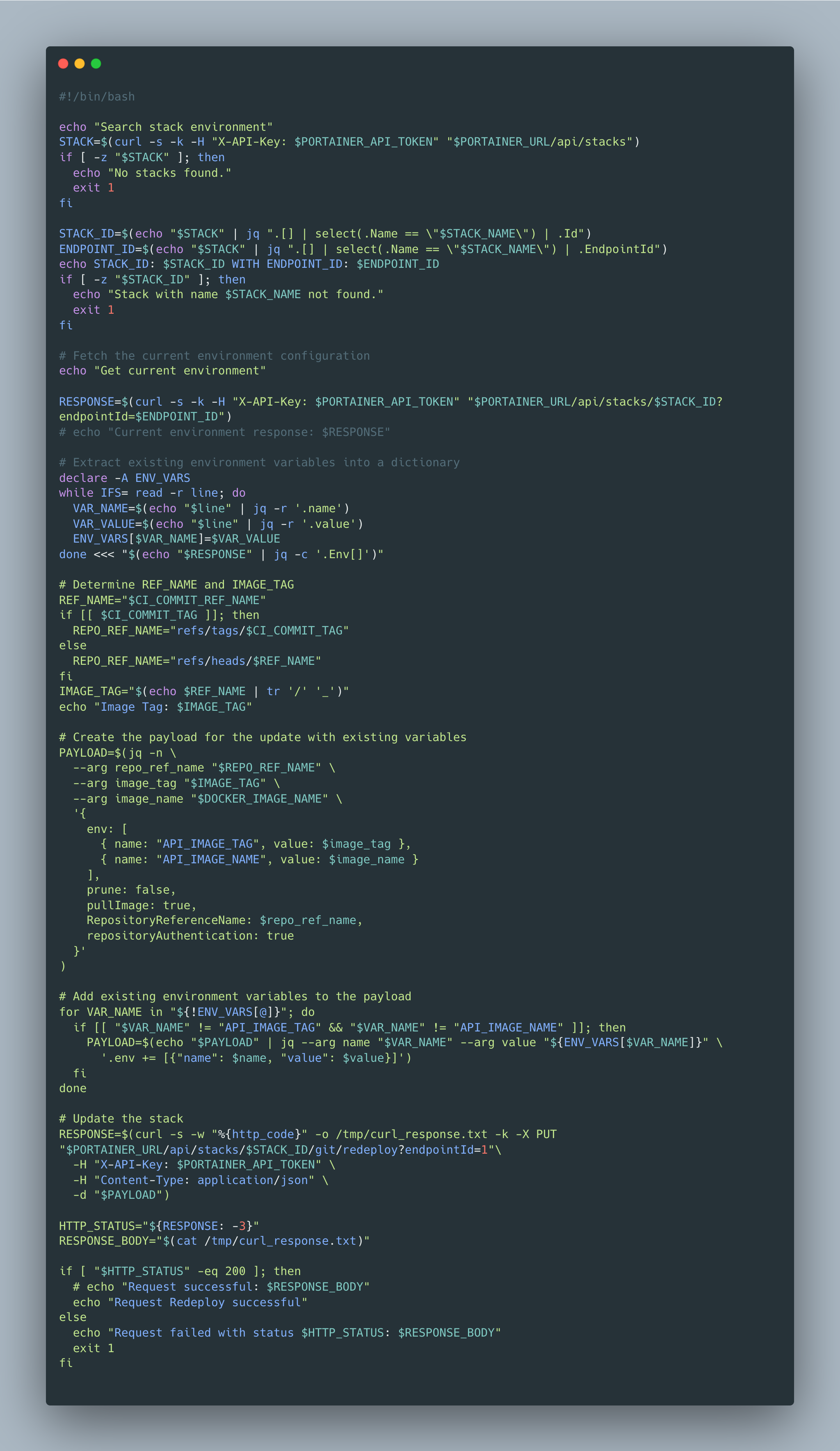
This process ensures that every code change leads to a repeatable and reliable deployment.
Using Portainer API for Scripting
Portainer CE offers a REST API that can be used to script deployment actions. For example, you can:
- Deploy or update stacks programmatically.
- Query container health and restart failed services.
- Automate routine management tasks such as cleaning unused images or networks.
By integrating these API calls into automation scripts, teams can achieve fine-grained control over deployment workflows.
Best Practices for Automated Deployments
- Keep Configurations in Git: Treat deployment files as code for better tracking and collaboration.
- Secure Secrets: Use secret management tools (e.g., Infisical, Vault) instead of hardcoding sensitive data.
- Test in Stages: Automate deployments progressively from dev to staging to production.
- Monitor Continuously: Combine automation with monitoring tools to catch issues early.
Conclusion
Automating application deployment with Portainer CE transforms container management from a manual, error-prone process into a streamlined and reliable workflow. Whether through stack files, CI/CD integration, or API-driven scripts, Portainer CE helps development teams deliver faster, safer, and more consistent deployments.
As automation continues to be a cornerstone of modern DevOps practices, Portainer CE stands out as a practical and approachable solution for organizations of all sizes.